This comprehensive guide is designed to help you understand ACH (Automated Clearing House) payments, a popular electronic payment system in the US. Whether you are a business owner looking to offer ACH as a payment option for your customers or an individual wanting to make recurring payments, this guide will provide you with all the necessary information.
What is ACH?
ACH payments are a type of electronic funds transfer (EFT) that allows money to be moved between bank accounts securely and efficiently. ACH transactions can be used for both credit transfers, where money is transferred from one account to another, and debit transfers, where money is withdrawn from an account.
History of ACH Payments
ACH payments were introduced in the United States in 1974 as an alternative to paper checks. The National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA) was established to oversee and regulate ACH transactions, making them a safe and reliable way to transfer funds.
How does ACH work?
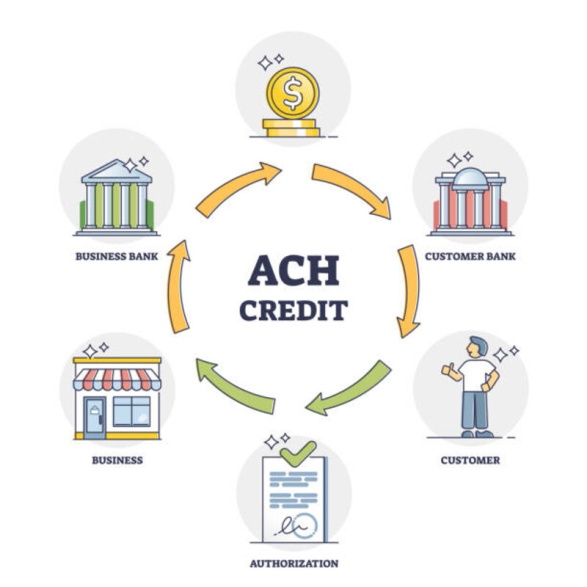
ACH works by using batch processing to transfer funds between bank accounts. This means that multiple transactions are grouped together and sent in a batch, making it a more cost-effective option for businesses compared to processing individual transactions.
To initiate an ACH payment, one party authorizes an originator (such as their employer or a company they want to pay) to debit or credit their account. The originator then sends this information to the ACH network, which processes and settles the transactions between banks.
Role of Various Parties in ACH Transactions
There are three main parties involved in an ACH transaction, each with their own role to play:
- Originator: The party who initiates the payment and authorizes the transfer of funds.
- Receiver: The party who receives the funds through ACH.
- ACH Operator: The organization responsible for facilitating the electronic transfer of funds between banks.
Types of ACH Payments
ACH Debits
ACH debits are used to withdraw money from a consumer's account for payments such as bills, loans, or subscriptions. These types of payments can be one-time or recurring.
ACH Credits
ACH credits are used to deposit funds into a consumer's account, such as direct deposits of salaries, tax refunds, or government benefits.
ACH Pre-Authorized Credits (PAC)
ACH Pre-Authorized Credits are used for recurring payments, such as membership fees or subscription services. This allows the consumer to authorize a company to withdraw funds from their account at regular intervals.
ACH Corporate Payments
ACH corporate payments are used for business-to-business transactions, such as payroll, vendor payments, and tax payments.
How to Set Up ACH Payments?
For Businesses
If you are a business looking to offer ACH payments as an option for your customers, you will need to set up an account with a financial institution that offers ACH services. This can be done through your existing bank or through a third-party payment processor.
Once your account is set up, you will need to obtain authorization from each customer to initiate the ACH debit or credit. This can be done through a signed form or an online authorization process.
For Individuals
To make ACH payments as an individual, you will need to provide your bank account information to the originator (such as your employer or biller). They will then use this information to initiate the ACH transaction and deduct funds from your account for payment. You can also set up automatic payments for recurring bills through your bank's online banking system.
Benefits of ACH Payments

There are several benefits to using ACH payments, including:
- Cost-effective: ACH payments typically have lower transaction fees compared to credit or debit card payments.
- Convenience: With Direct Deposit and Direct Payment, you can avoid the hassle of writing and mailing checks.
- Security: ACH transactions are highly secure, as they require authorization and follow strict regulations to protect against fraud.
- Efficiency: The batch processing system allows for faster and more efficient payment processing.
Drawbacks and Risks of ACH Payments
While there are many benefits to using ACH payments, it's important to be aware of the potential drawbacks and risks involved, including:
- Processing Time: It can take a few days for ACH transactions to clear and for funds to be transferred between accounts.
- Insufficient Funds: If there are not enough funds in the account at the time of an ACH debit, the transaction may be declined and a fee may be charged.
- Fraud: As with any electronic payment system, there is always a risk of fraud. It's important to ensure you are working with reputable companies and have proper security measures in place to protect against fraudulent activity.
Common Use Cases for ACH Payments
ACH payments are commonly used in various scenarios, including:
- Payroll processing for employee salaries.
- Direct deposits of government benefits and tax refunds.
- Payment of recurring bills like rent/mortgage, utilities, subscriptions, etc.
- Business-to-business transactions such as vendor payments and tax payments.
Future of ACH Payments
With the rise of digital payments, ACH transactions are becoming increasingly popular. The ACH network has continued to evolve and adapt to meet the changing needs of businesses and consumers. In the future, we may see advancements in technology that make ACH payments even faster and more secure.
Conclusion
ACH payments have become an integral part of today's financial landscape, offering a convenient and secure way to transfer funds between bank accounts. As technology continues to advance and the demand for digital payments grows, we can expect ACH transactions to play an even larger role in our daily lives. So next time you make a payment or receive a deposit via ACH, remember the history and process behind this efficient method of transferring funds. So, ACH payments are here to stay and will continue to play a significant role in the world of finance.




